Wi-Fi interface profiles
⚠ IMPORTANT:
The WiFI profiles are only valid and processed by the device if the Virtual Ethernet-WiFi Bridge is disabled.
🎯 HINT:
It isHIGHLY recommended to only use ONE WiFi interface profile as deep network technology knowledge is required to configure multiple profiles.
General Wi-Fi preferences

Profile name
Wireless connection
Automatically join this network when available
Connection Priority
Range: 0 .. 1000
Number of connection retries
Operating mode & Security
Hotspot configuration

SSID
default: CR3171_<<LAST 4 DIGITS OF MAC>>
Hide SSID
default: OFF
Security type
Key management configuration for the WiFi connection.
Options:
unencrypted, No further setting required WPA/PSK,SAE, OWE, WPA/EAP
🎯 TIP :
More information what the options means is described below.
Password
WPA/PSK SAE unencrypted OWE EAP
🎯 TIP :
More information about the various security types:
WPA/PSK: Wikipedia - WPA terminology
OWE: Wikipedia - Opportunistic Wireless Encryption
SAE: Wikipedia - Simultaneous Authentication of Equals
WPA/EAP: Wikipedia - Extensible Authentication Protocol
In case of security type SAE
WPA/EAP
Username
Password
Anonymous identity
Domain
CA Certificate
Client configuration
SSID
default: CR3171_<<LAST 4 DIGITS OF MAC>>
SSID of the Wi-Fi network.
Security type
Security type
Options:
unencrypted, No further setting required WPA/PSK, SAE, OWE, WPA/EAP
Password
WPA/PSK Pre-Shared Key
In case of security type SAE , the password will be handled according to the SAE Authentication method.
EAP
When the WPA/EAP (Extinsible Authentication Protocol) option is chosen, some more settings has to be entered.
Username
SAE EAP
When the
WPA/EAP Username
Available when security type is set to WPA/EAP, is the EAP Username.
Password
Password
Anonymous identity
Domain
CA Certificate
Ad-hoc configuration
ad-hoc
Security type
Options:
unencrypted, No further setting required WPA/PSK, SAE, OWE, WPA/EAP
Password
In case of security type SAE, the password will be handeled according to the SAE Authentication method.
Band and IP configuration method
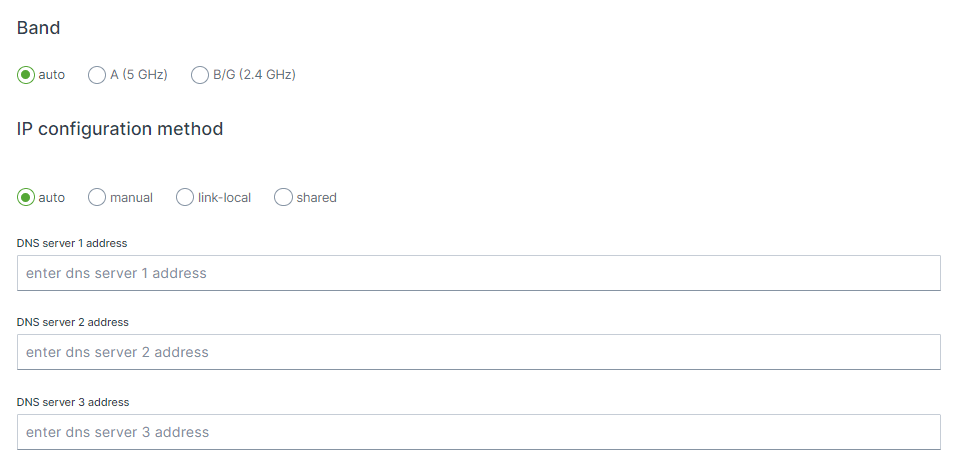
Band
IP configuration method
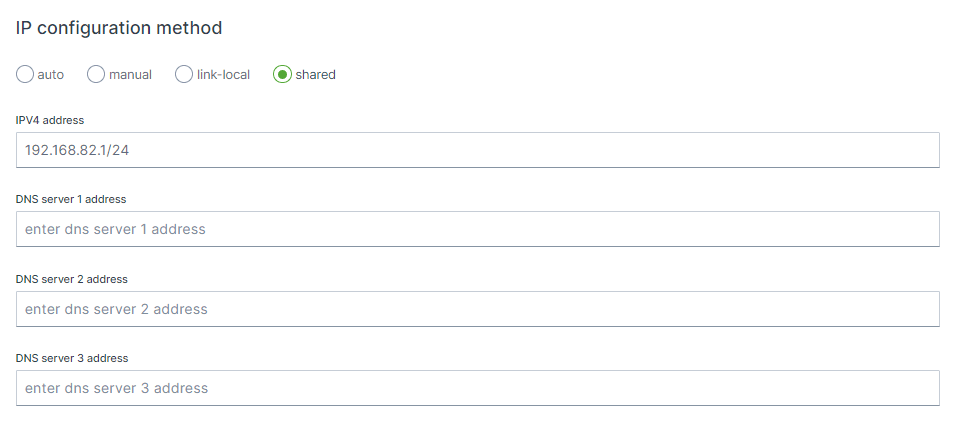
Selector
auto, the interface will be configured as DHCP client and therefore will be assigned a IP address from an external DHCP router. manual, static IP settings will be used, link-local, a link-local address is a network address that is valid only for communications on a local link, i.e. within a subnetwork that a host is connected to shared, interface is set to act as a DHCP server.
Channel
Wireless channel to use for this connection, the value of zero means, that the channel will be chosen automatically. Explicitly setting this option will ensure that the device only joins a network on the specified channel.
manual, static IP settings will be used,
shared, the default, interface is set to act as a DHCP server.
IPV4 Address
By using e.g. 192.168.82.1/24 the device will be part of the 192.168.82.0 network and will allow access or communication from IPs in the range of 192.168.82.1 - 192.168.82.255
🎯 TIP:
As security measure it is advisable to tighten the allowed IPs on the network as possible, for instance to use /29 or 255.255.255.248 subnet to only allow 6 address on the network, as 192.168.82.0 is the network address and 192.168.82.7 is the broardcast address and 192.168.82.1 - 192.168.82.6 remains available.